Conquering AP Physics C Rotational Motion FRQs
Ever felt that dizzying sensation when thinking about rotational motion problems on the AP Physics C exam? You're not alone. Many students find the free-response questions (FRQs) on this topic particularly challenging. But what if I told you that with the right approach, these daunting questions could become manageable, even conquerable? This article aims to provide you with the tools and insights you need to confidently approach AP Physics C rotation FRQs.
The AP Physics C exam is renowned for its rigor, pushing students to apply their understanding of complex physics principles. Within the Mechanics section, rotational motion represents a significant portion, often appearing in FRQs. These questions delve into concepts like torque, angular momentum, moment of inertia, and rotational kinetic energy. Mastering these concepts is crucial for success on the exam.
The inclusion of rotational motion in the AP Physics C curriculum stems from its fundamental importance in understanding how the physical world works. From the spin of a figure skater to the rotation of planets, rotational motion is everywhere. The FRQs assess not just your knowledge of formulas but also your ability to analyze real-world scenarios and apply these concepts to solve problems.
A common struggle students face with AP Physics C rotation FRQs is connecting the abstract concepts to concrete problem-solving strategies. Many get bogged down in the mathematics and lose sight of the underlying physics principles. Another challenge is visualizing the rotational motion itself, which can make it difficult to set up the problem correctly. This article will address these challenges head-on, providing clear explanations and practical tips.
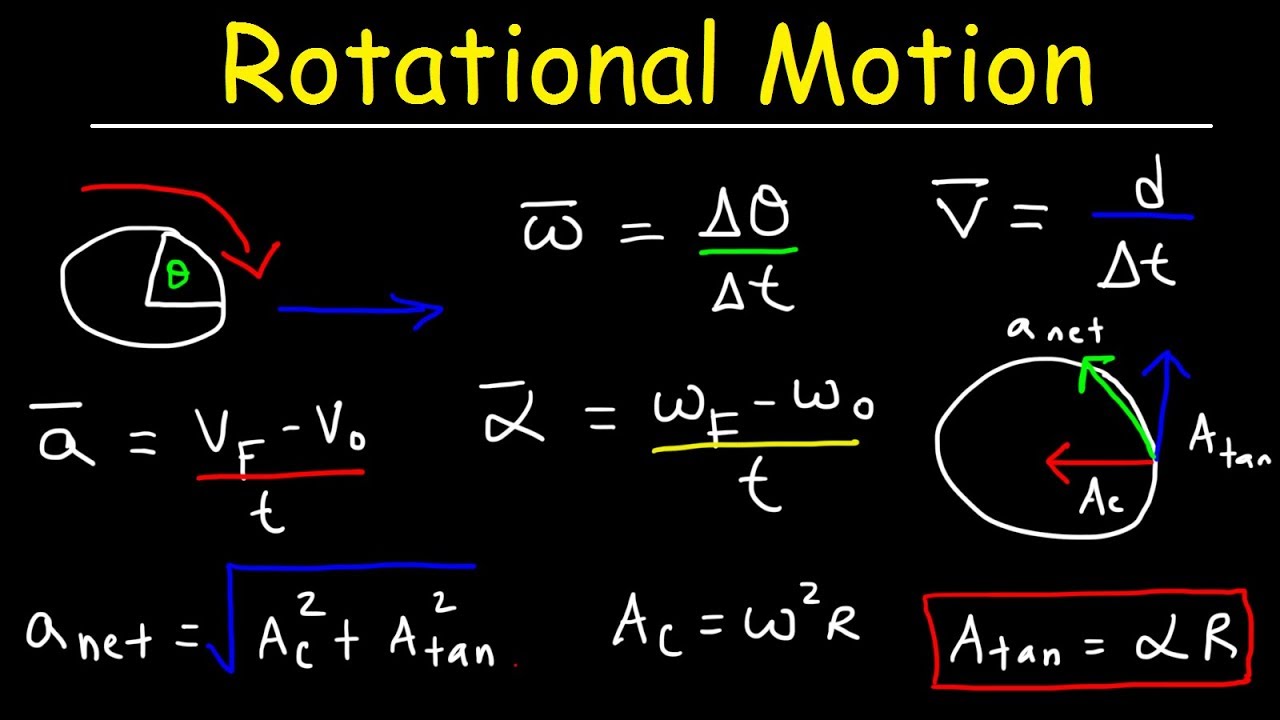
Let's start by demystifying some key terms. Torque, often described as rotational force, causes changes in rotational motion. Angular momentum, analogous to linear momentum, is a measure of an object's tendency to keep rotating. Moment of inertia represents an object's resistance to changes in rotational motion. And rotational kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its rotation. Understanding these concepts is the foundation for tackling any rotation FRQ.
A simple example is a spinning top. The torque applied by your hand starts the top spinning. As it spins, it possesses angular momentum. The top's shape and mass distribution determine its moment of inertia. And the faster it spins, the greater its rotational kinetic energy.
One benefit of mastering rotational motion is its applicability to other physics topics. Understanding concepts like angular momentum can be crucial when studying topics such as planetary motion or the behavior of subatomic particles. Moreover, the problem-solving skills honed while tackling rotation FRQs are transferable to other areas of physics and beyond.
Another advantage is the practical application of these concepts in engineering and other fields. Designing anything from a car engine to a wind turbine requires a deep understanding of rotational motion.
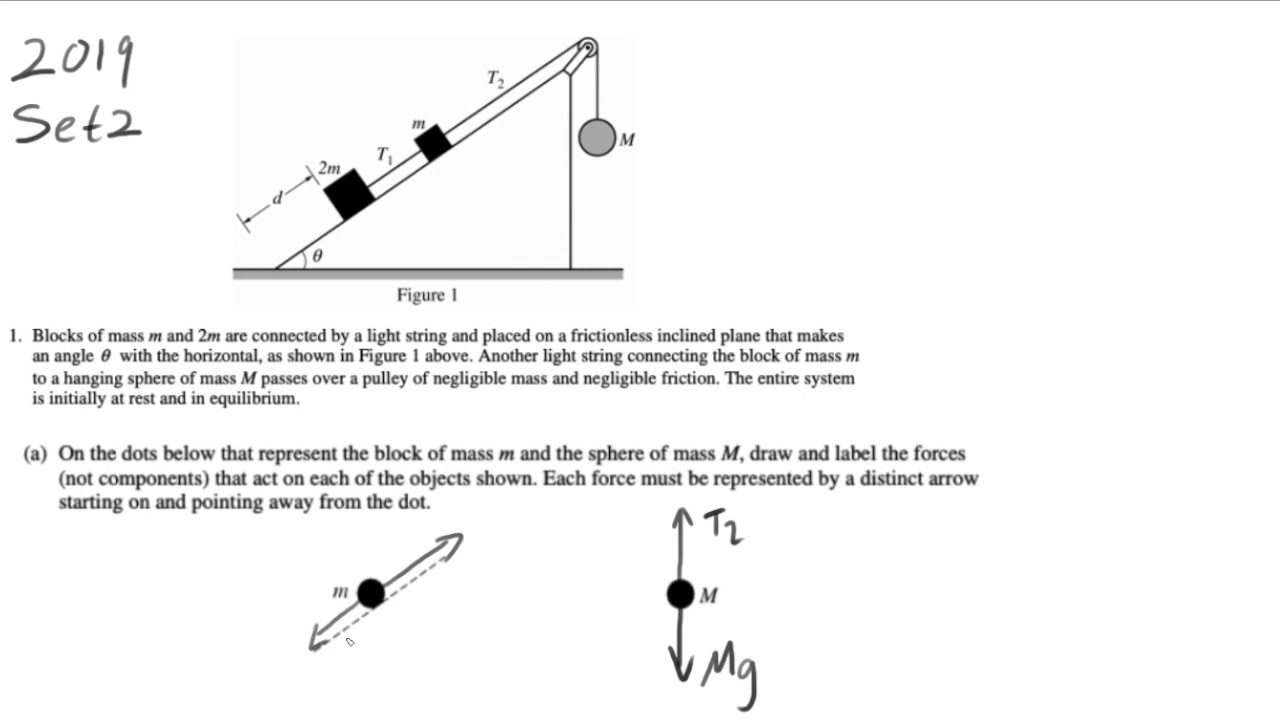
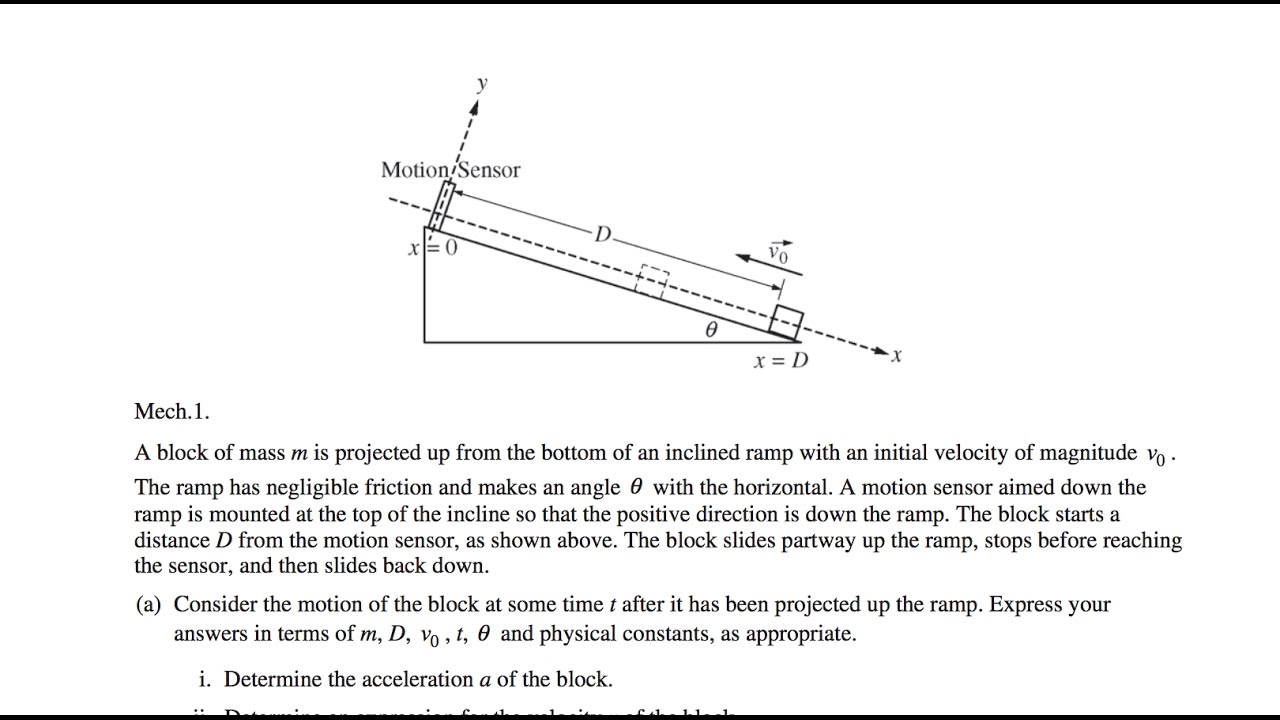
To tackle an AP Physics C rotation FRQ effectively, start by identifying the given information and the unknown quantities you need to find. Draw a clear diagram of the system, labeling all relevant forces and distances. Choose the appropriate equations based on the concepts involved. Solve the equations systematically, paying attention to units and significant figures.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AP Physics C Rotation FRQs
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Deepens understanding of fundamental physics concepts | Can be challenging and time-consuming |
| Develops strong problem-solving skills | Requires strong mathematical background |
| Prepares for college-level physics courses | Contributes to overall exam pressure |
A common challenge is dealing with complex geometries. Break down complex shapes into simpler ones to calculate the moment of inertia. Another challenge is choosing the correct axis of rotation. Carefully analyze the problem to identify the axis around which the object is rotating.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is torque? - Torque is the rotational equivalent of force.
2. What is angular momentum? - Angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum.
3. What is the moment of inertia? - Moment of inertia is a measure of an object's resistance to rotational acceleration.
4. What is rotational kinetic energy? - Rotational kinetic energy is the kinetic energy due to an object's rotation.
5. How do I calculate torque? - Torque is calculated as the cross product of the force vector and the displacement vector from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied.
6. How do I calculate angular momentum? - Angular momentum is calculated as the product of the moment of inertia and the angular velocity.
7. How do I calculate the moment of inertia? - The moment of inertia depends on the object's shape and mass distribution. Formulas exist for common shapes.
8. How do I calculate rotational kinetic energy? - Rotational kinetic energy is calculated as one-half times the moment of inertia times the square of the angular velocity.
One tip for success is to practice regularly with past FRQs. This will familiarize you with the types of questions asked and help you develop a systematic approach to problem-solving. Another tip is to focus on understanding the underlying physics concepts rather than just memorizing formulas.
In conclusion, AP Physics C rotation FRQs can seem intimidating, but with dedicated effort and the right strategies, they become manageable. By focusing on understanding the core concepts, practicing regularly, and developing a systematic approach to problem-solving, you can conquer these challenges and achieve success on the AP Physics C exam. The ability to analyze and solve rotational motion problems is not just crucial for the exam but also provides a valuable foundation for further studies in physics, engineering, and other related fields. So, embrace the challenge, and you'll find that understanding rotational motion can be a truly rewarding experience. Start practicing today and unlock your potential in this fascinating area of physics.
Craigslist fort myers florida your local marketplace
Ea sports fc 24 update 13 deep dive
Unraveling the enigma of shadow slave light novel chapter 1205