Decoding Medicare Part B Costs: Your Guide to 2024 Premiums and Beyond
Navigating the labyrinthine world of healthcare costs can feel like traversing a digital desert, parched for clarity. One particularly perplexing oasis (or mirage?) is Medicare Part B insurance. How much does it cost? The question echoes across countless online forums, whispered in doctor's waiting rooms, and pondered over kitchen tables. This deep dive explores the intricacies of Part B pricing, offering a roadmap to understanding this crucial aspect of healthcare coverage for those 65 and older, and certain younger individuals with disabilities.
Medicare Part B, the bedrock of outpatient medical coverage, helps pay for services like doctor visits, outpatient hospital care, preventive services, and some medical equipment. Unlike Part A (hospital insurance), Part B isn't free for most people. Understanding the cost of Part B is essential for effective financial planning in retirement and beyond.
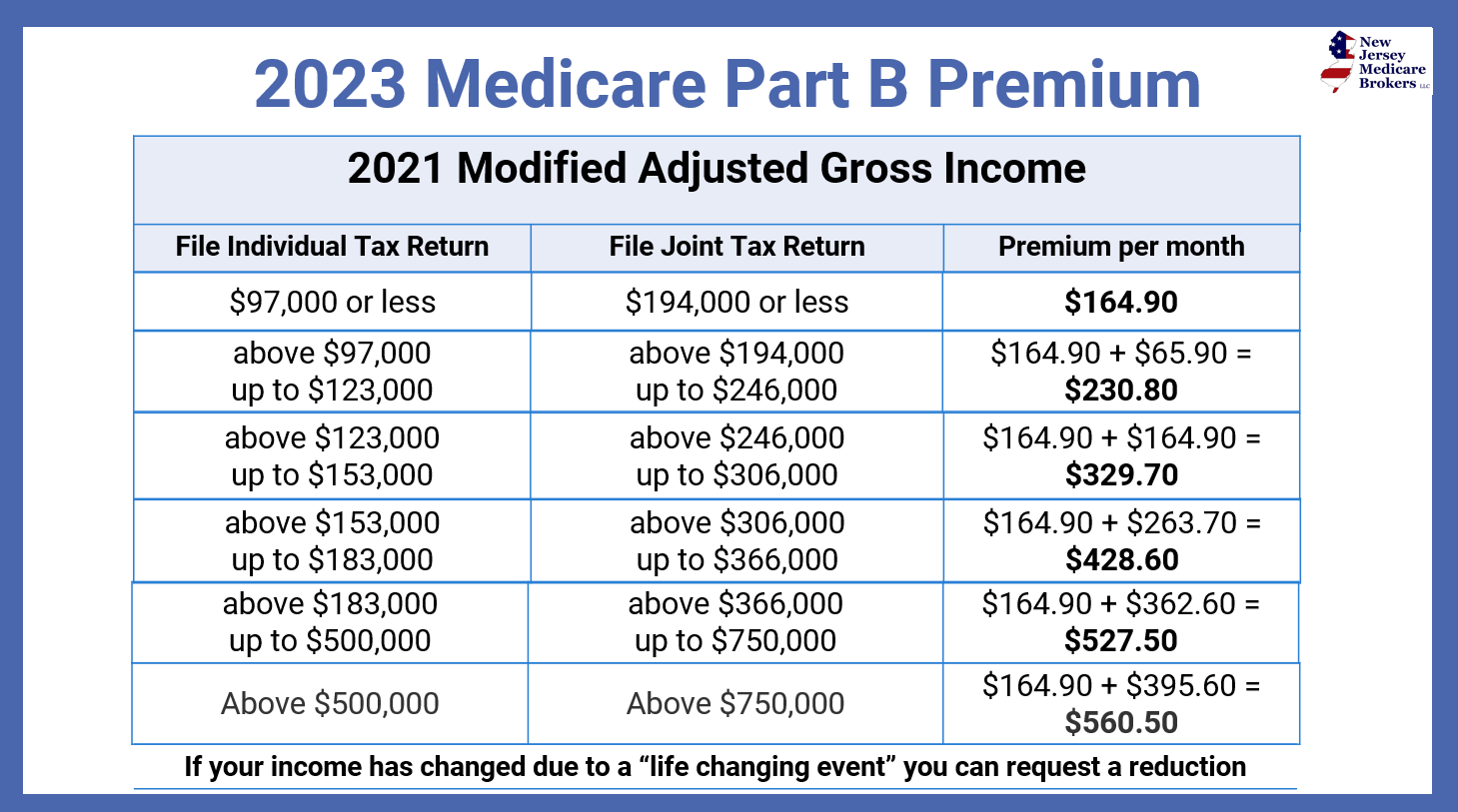
The cost of Part B coverage hinges primarily on the standard monthly premium. This premium is influenced by your income, reported to the Social Security Administration via your tax return. Higher earners pay a higher premium, a system known as Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA). The base premium is set annually, and changes can ripple across beneficiaries' budgets.
Historically, Part B costs have been subject to adjustments, often reflecting the rising costs of healthcare services. The program's origins trace back to the 1965 enactment of Medicare, aimed at providing a safety net for healthcare expenses during retirement. The importance of Part B lies in its coverage of essential medical services that contribute significantly to overall health and well-being, from routine checkups to specialized treatments.
One of the primary issues surrounding Part B pricing is the complexity of calculating the premium based on income. Determining the correct IRMAA tier can be confusing for some beneficiaries, and unexpected premium increases can strain household budgets. The dynamic nature of healthcare costs further complicates predictions and planning for future expenses.
Several factors influence Part B premiums. Your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) is a key driver, as higher MAGI typically results in higher premiums. Other factors influencing the cost of Medicare Part B include legislative changes, inflation in healthcare spending, and utilization patterns.
Understanding the various components of Part B costs is paramount. The standard monthly premium is the most prominent expense, but other costs may arise. These include the annual deductible, coinsurance (generally 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most services), and copayments for specific services.
Benefit 1: Broad coverage for outpatient services. Part B helps pay for crucial medical needs, from routine doctor visits to specialized tests and treatments, providing financial peace of mind.
Benefit 2: Preventive care coverage. Part B covers many preventive services, like annual wellness visits and screenings, promoting proactive health management and early detection of potential issues.
Benefit 3: Access to a wide network of providers. Beneficiaries can choose from a vast network of doctors and healthcare professionals who accept Medicare assignment, ensuring flexibility and choice in care.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Medicare Part B
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive outpatient coverage | Monthly premiums |
| Access to preventive services | Deductibles and coinsurance |
| Large network of providers | Premium increases based on income (IRMAA) |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How much does Part B cost in 2024?
A: The standard monthly premium for Part B in 2024 is $[Insert 2024 Premium when available], but it can vary based on income.
Q2: How is the Part B premium calculated?
A: The premium is based primarily on your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) from two years prior.
Q3: What is IRMAA?
A: IRMAA stands for Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount and refers to the additional premium paid by higher-income earners.
Q4: What services does Part B cover?
A: Part B covers a wide range of outpatient services, including doctor visits, tests, and some medical equipment.
Q5: What is the Part B deductible?
A: The annual Part B deductible is $[Insert 2024 Deductible when available].
Q6: How do I enroll in Part B?
A: You can typically enroll in Part B during your Initial Enrollment Period around your 65th birthday or during a Special Enrollment Period if you have qualifying coverage through an employer.
Q7: Can I appeal my IRMAA determination?
A: Yes, you can appeal if you believe your IRMAA is incorrect due to a life-changing event.
Q8: Where can I find more information about Part B costs?
A: You can visit the official Medicare website (Medicare.gov) for detailed information on Part B costs and coverage.
In conclusion, understanding the cost of Medicare Part B is crucial for anyone approaching retirement or currently enrolled in the program. The price of Part B, influenced by factors like income and healthcare costs, impacts financial planning and access to essential medical services. By navigating the complexities of premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage and budget effectively. Exploring resources like the official Medicare website and consulting with financial advisors can empower beneficiaries to optimize their healthcare spending and secure the coverage they need. Don’t navigate the Medicare maze alone. Equip yourself with knowledge and take control of your healthcare future.
Unlocking the secret code the power of alt key emoticons
Conquer the georgia dmv test ace your permit
Mastering dexter 3500 lb axle lug nut torque your guide to safe towing