Global Alcohol Consumption Patterns
Around the world, the clinking of glasses and the sharing of drinks are often integral parts of social gatherings and cultural traditions. But behind these familiar rituals lies a complex tapestry of alcohol consumption patterns that vary significantly from country to country. Understanding these variations is crucial for public health initiatives, policy development, and even for travelers seeking to navigate cultural norms.
What drives these differences in alcohol intake across borders? Factors like cultural norms, religious beliefs, economic conditions, and government policies all play a role in shaping a nation's relationship with alcohol. Examining these influences helps us understand why some countries boast high per capita alcohol consumption, while others maintain significantly lower levels.
The historical context of alcohol consumption also provides valuable insights. From ancient winemaking traditions to the rise of modern brewing techniques, the history of alcoholic beverages is intertwined with the history of human civilization. Understanding this historical context can shed light on present-day drinking habits and their societal impact.
The significance of studying alcohol consumption by country extends beyond mere curiosity. It provides crucial data for public health organizations working to address alcohol-related harm. By analyzing trends and identifying at-risk populations, targeted interventions can be developed to promote responsible drinking and mitigate the negative consequences of excessive alcohol use.
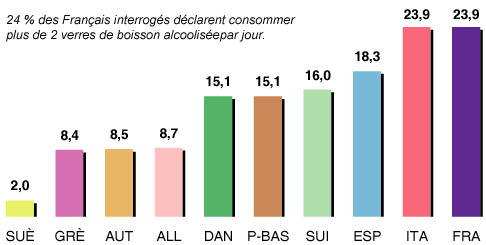
Exploring per-capita alcohol consumption provides a snapshot of overall trends, but it’s important to remember that these figures represent averages. Within any given country, there will be variations in drinking habits based on factors such as age, gender, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. Deeper dives into the data are necessary to paint a more comprehensive picture.
Historically, alcohol has played a diverse role in societies worldwide. From ceremonial uses to social lubrication, alcoholic beverages have been integrated into countless cultural practices. However, the history of alcohol consumption is not without its dark chapters, including periods of prohibition and widespread societal problems related to excessive drinking.
One of the main issues associated with alcohol consumption is its potential impact on public health. Excessive alcohol use can lead to a range of health problems, including liver disease, heart disease, certain types of cancer, and mental health issues. Understanding these risks is crucial for promoting responsible drinking habits and developing effective public health strategies.
Several organizations provide valuable resources for understanding alcohol consumption patterns and promoting responsible drinking. The World Health Organization (WHO) offers comprehensive data and reports on global alcohol consumption and its health implications. National institutes of health in many countries also provide valuable information and resources specific to their region.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Studying Alcohol Consumption by Country
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Provides insights for public health initiatives | Data may not fully capture informal alcohol consumption |
| Helps inform policy decisions | Cultural nuances can be difficult to quantify |
| Facilitates cross-cultural comparisons | Data availability may vary between countries |
Alcohol consumption patterns can be complex, but understanding the factors that influence them is essential for promoting health and well-being worldwide. By examining historical trends, cultural influences, and public health implications, we can work towards creating a healthier relationship with alcohol on a global scale.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is per capita alcohol consumption?
A measure of the average alcohol consumed per person in a given population.
2. How is alcohol consumption data collected?
Through surveys, sales data, and production statistics.
3. What are the health risks associated with excessive alcohol use?
Liver disease, heart disease, certain cancers, and mental health issues.
4. How can I find alcohol consumption data for a specific country?
Consult resources like the WHO or national health institutes.
5. What are some effective strategies for promoting responsible drinking?
Public awareness campaigns, education programs, and policy interventions.
6. How do cultural norms influence alcohol consumption?
Cultural traditions and beliefs can shape attitudes towards alcohol.
7. What is the role of government policies in regulating alcohol consumption?
Policies can influence availability, pricing, and advertising of alcohol.
8. Where can I find support for alcohol-related problems?
Contact local health services or support organizations.
In conclusion, understanding alcohol consumption by country is vital for a multitude of reasons. It allows us to gain insights into the complex interplay of cultural, historical, and economic factors that shape drinking habits worldwide. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective public health interventions, crafting informed policies, and fostering a more nuanced understanding of global cultures. By examining alcohol consumption patterns, we can work towards minimizing the harms associated with excessive alcohol use and promoting a healthier relationship with alcohol across the globe. This understanding also empowers individuals to make informed choices about their own alcohol consumption and contribute to a culture of responsible drinking. Moving forward, continued research and international collaboration are essential to further refine our understanding of this complex issue and develop effective strategies for promoting health and well-being on a global scale. We encourage everyone to learn more about alcohol consumption patterns in their own communities and to support initiatives that promote responsible drinking habits.
Illuminating simplicity malibu 7 watt light bulbs
Maximize ac performance understanding ac system evacuation
Unlocking value in st charles county your guide to buy sell trade