Unlocking the Secrets of Air Source Heat Pumps
Want a heating system that's both eco-friendly and cost-effective? Air source heat pumps are gaining popularity, and for good reason. They offer a clever way to heat (and often cool) your home by transferring heat from the outside air, even when it's cold. But how do these systems actually work? Let's dive into the mechanics of air source heat pump heating.
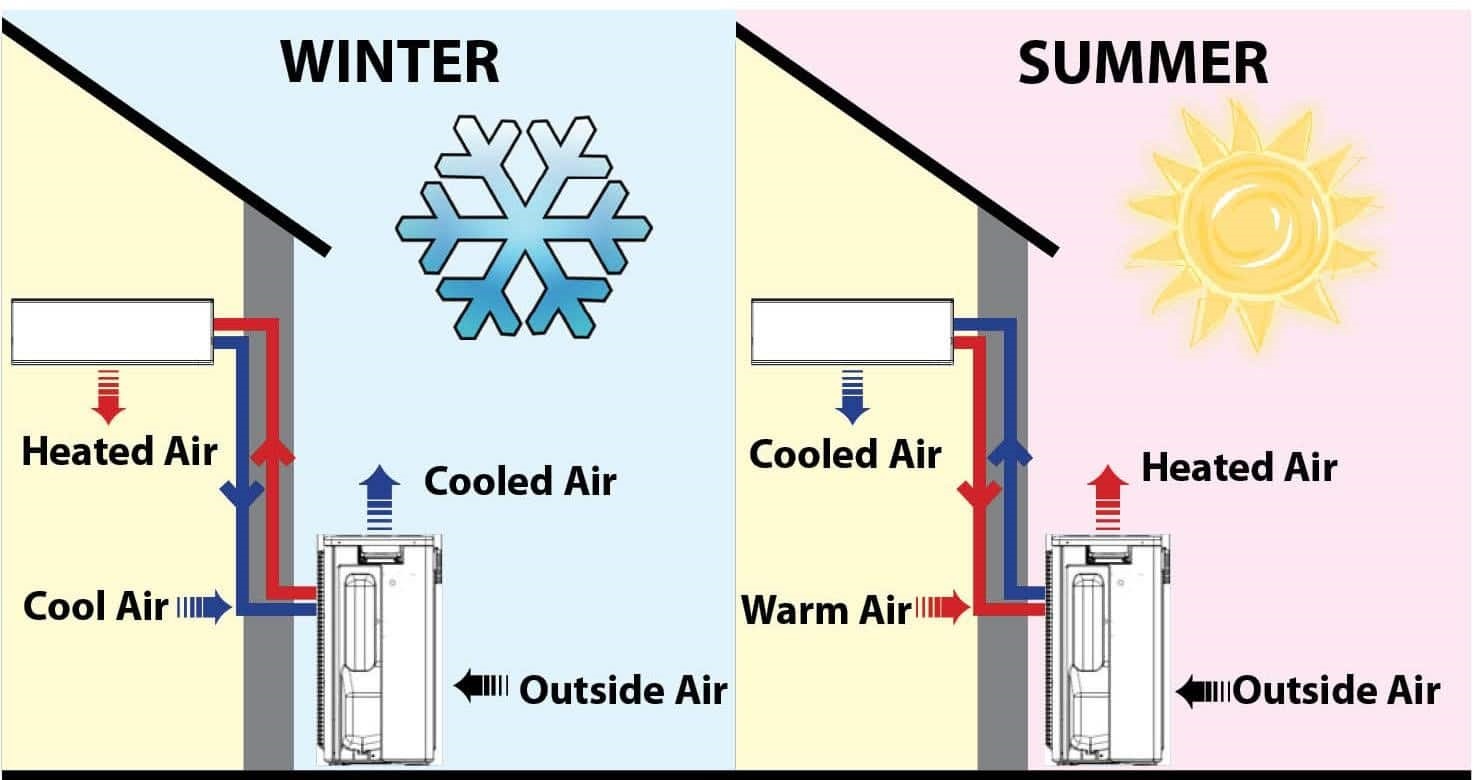
Imagine your refrigerator, but in reverse. That's the basic principle behind an air source heat pump. Instead of moving heat out of your fridge and into your kitchen, a heat pump extracts heat from the outdoor air and brings it inside to warm your home. Surprisingly, these systems can extract heat even from cold winter air. This process utilizes a refrigerant that absorbs and releases heat as it changes between liquid and gas states.
The operation of an air source heat pump involves a cycle with key components. An outdoor unit containing a fan, evaporator coil, and compressor works in tandem with an indoor unit housing a condenser coil and another fan. The refrigerant circulates between these two units, absorbing heat from the outside air and releasing it inside your home.
The history of heat pump technology dates back to the mid-19th century, but the widespread adoption of air source heat pumps for residential heating is a more recent phenomenon driven by increasing energy costs and environmental concerns. These systems offer a significant advantage over traditional heating methods by using electricity to move heat rather than generating it directly, resulting in greater energy efficiency.
Understanding how an air source heat pump operates is crucial for homeowners considering this technology. Key factors to consider include the climate, proper sizing of the unit for the home, and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. A well-maintained air source heat pump can provide years of reliable and efficient heating.
The refrigerant within the system plays a crucial role. It absorbs heat from the outside air, even in cold temperatures. This heat causes the refrigerant to evaporate and become a gas. The gas is then compressed, raising its temperature significantly. This hot gas travels to the indoor unit, where it releases its heat into your home's air through the condenser coil.
Benefits of using air source heat pumps include energy efficiency, reduced operating costs compared to traditional heating systems, and a smaller environmental footprint due to lower greenhouse gas emissions. For example, a homeowner switching from an oil furnace to an air source heat pump can experience significant savings on their heating bills.
Before installing an air source heat pump, consider factors like climate suitability, home insulation, and available space for the outdoor unit. Consult with a qualified HVAC professional to determine the appropriate size and type of heat pump for your needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Air Source Heat Pumps
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Energy-efficient | Lower efficiency in extreme cold |
| Environmentally friendly | Higher upfront cost |
| Heating and cooling capabilities | May require supplemental heating in very cold climates |
Best practices for air source heat pump operation include regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing air filters and scheduling professional inspections. Ensuring proper airflow around the outdoor unit is also important.
Real-world examples of successful air source heat pump installations can be found in homes across various climates. Many homeowners have reported significant energy savings and improved comfort after switching to this technology.
Challenges with air source heat pumps can include reduced efficiency in extremely cold climates and potential noise from the outdoor unit. Solutions include supplemental heating systems and proper unit placement to minimize noise.
FAQs about air source heat pumps often address topics like efficiency in cold weather, maintenance requirements, and installation costs. Consulting with a qualified HVAC professional can provide personalized answers.
Tips for maximizing efficiency include ensuring proper insulation, sealing air leaks, and using programmable thermostats. These measures can further enhance the energy-saving benefits of an air source heat pump.
In conclusion, air source heat pumps offer a compelling solution for efficient and environmentally friendly home heating. By understanding how these systems operate, homeowners can make informed decisions about adopting this technology. The benefits of reduced energy consumption, lower operating costs, and a smaller carbon footprint make air source heat pumps a smart choice for those seeking a sustainable and cost-effective heating solution. Take the time to research and consult with professionals to determine if an air source heat pump is the right choice for your home. Investing in this technology can lead to long-term savings and contribute to a greener future. Consider exploring additional resources online or contacting local HVAC companies for personalized guidance and quotes. Embrace the future of home heating with the efficient and versatile technology of air source heat pumps.
Black clover anime and manga sync up explained
Need for speed payback online thrills challenges and community
Ford focus lug nut threads everything you need to know