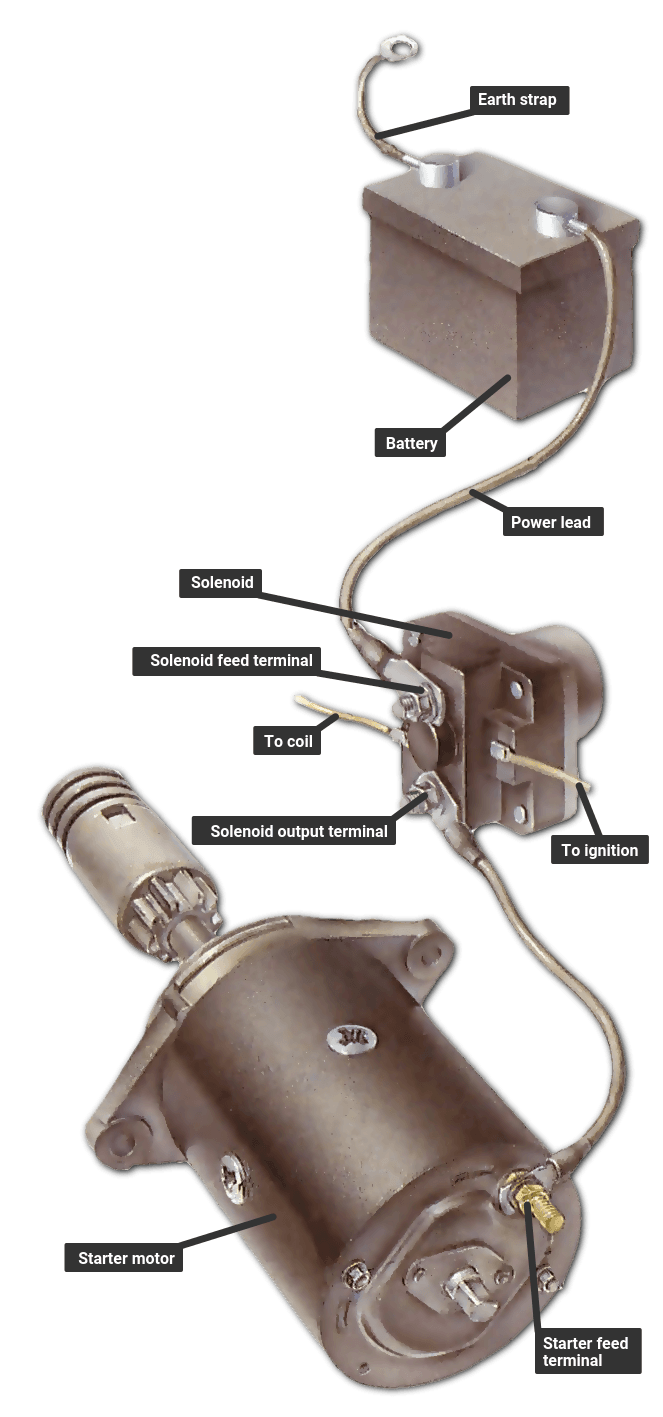
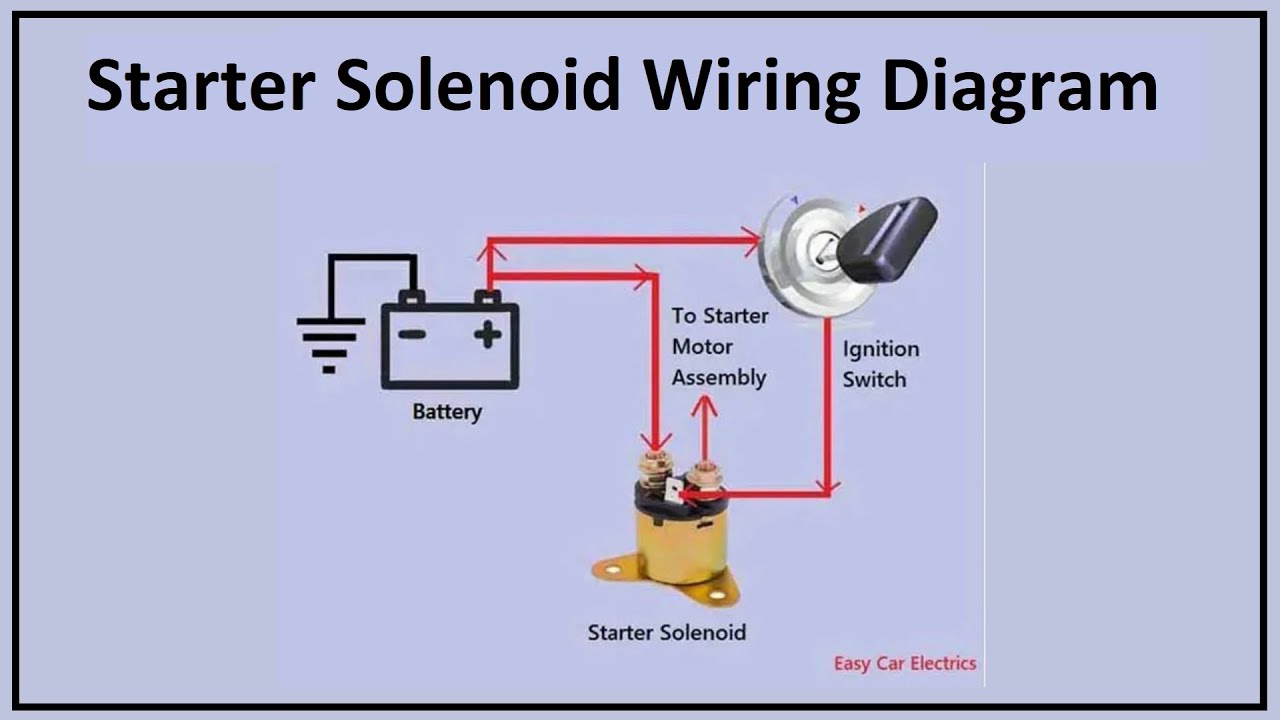
Unlocking the Secrets of the 4 Post Solenoid
Ever wondered how some machines achieve precise, powerful movements with just a pulse of electricity? The answer often lies within a compact yet powerful device: the 4 post solenoid. This article delves into the intricacies of this electromechanical marvel, unraveling the principles behind its operation and exploring its diverse applications.
A 4 post solenoid, in essence, is an electromagnet that converts electrical energy into linear motion. Unlike a simple two-post solenoid, the 4-post configuration offers increased stability and force, making it suitable for heavier loads and more demanding applications. Imagine it as a miniature electric motor, capable of generating a strong push or pull with remarkable precision.
The core components of a 4 post solenoid include a coil of wire wrapped around a magnetic core, a plunger or armature, and the four posts that guide the plunger’s movement. When an electric current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that pulls the plunger into the core. This linear movement is the key to the solenoid’s functionality.
Understanding the principles governing 4 post solenoid function is crucial for selecting the right solenoid for a specific application. Factors such as voltage, current, stroke length (the distance the plunger travels), and force output need careful consideration. Choosing the wrong solenoid can lead to inefficient operation or even damage to the equipment.
While the exact origins of the solenoid are debated, its principles are rooted in the early 19th-century discoveries of electromagnetism. Over time, the basic solenoid design has evolved, leading to the development of specialized versions like the 4 post solenoid to meet the growing demands of industrial automation, automotive systems, and various other fields. A major issue related to 4 post solenoids can be wear and tear of the plunger and posts, affecting performance. Regular maintenance and lubrication are crucial for ensuring longevity and reliability.
A key advantage of the 4 post configuration is its inherent stability. The four posts guide the plunger’s movement, preventing tilting or binding, which can occur in simpler two-post designs. This precise control makes them ideal for applications requiring accurate positioning.
Another benefit is the increased force output compared to two-post solenoids. The four posts distribute the load more effectively, allowing for the handling of heavier objects or the generation of stronger pushing or pulling forces.
The compact size of 4 post solenoids also makes them highly versatile. They can be easily integrated into complex machinery and systems where space is limited.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 4 Post Solenoids
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased stability and precise movement | Can be more complex to manufacture than 2-post solenoids |
| Higher force output | May require more space than a simpler solenoid in some cases |
| Compact size | Higher cost compared to 2-post solenoids |
Best Practices:
1. Choose the right solenoid for the application, considering factors like voltage, current, stroke length, and force output.
2. Ensure proper lubrication of the plunger and guide posts to minimize wear and tear.
3. Protect the solenoid from excessive heat and moisture to prevent damage to the coil and other components.
4. Use appropriate wiring and connectors to ensure reliable electrical connections.
5. Regularly inspect the solenoid for signs of wear or damage.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the difference between a 2-post and a 4-post solenoid? (Stability and force)
2. How does the current affect the solenoid’s operation? (Strength of magnetic field)
3. What is the role of the plunger? (Converts magnetic force into linear motion)
4. How do I choose the right solenoid for my application? (Consider voltage, current, stroke, force)
5. What are common problems with solenoids? (Wear and tear, overheating)
6. How can I extend the lifespan of a solenoid? (Proper lubrication and maintenance)
7. What are some examples of 4-post solenoid applications? (Industrial automation, automotive)
8. Where can I find more information on solenoid specifications? (Manufacturer datasheets)
Tips and Tricks: Use a diode across the solenoid coil to suppress voltage spikes when the solenoid is de-energized. Consider using a solenoid driver circuit for precise control over the current and timing.
In conclusion, the 4 post solenoid plays a critical role in countless applications, providing a reliable and efficient way to convert electrical energy into precise linear motion. Its robust design, increased stability, and higher force output make it a valuable component in various industries. By understanding the principles behind its operation, selecting the right solenoid for the job, and following best practices for maintenance, you can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of these electromechanical workhorses. Understanding the nuances of 4 post solenoid function is essential for anyone working with automated systems, robotics, or any application that requires precise and powerful linear actuation. From automotive systems to industrial machinery, these compact devices provide the muscle behind countless automated processes. Invest time in understanding these essential components and unlock the potential of precise, electrically controlled movement.
Transform your space with deep enchanting dark warm green paint
Lined shorts and underwear the comfort question
That annoying popping sound when turning your car